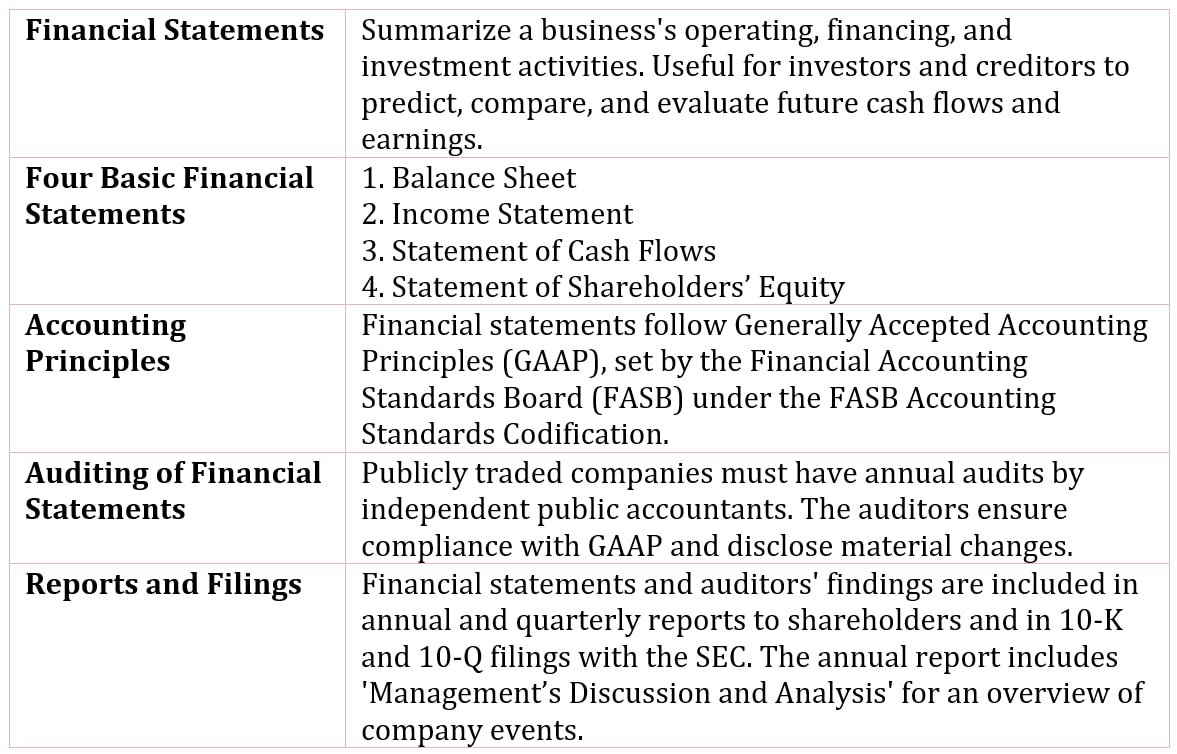
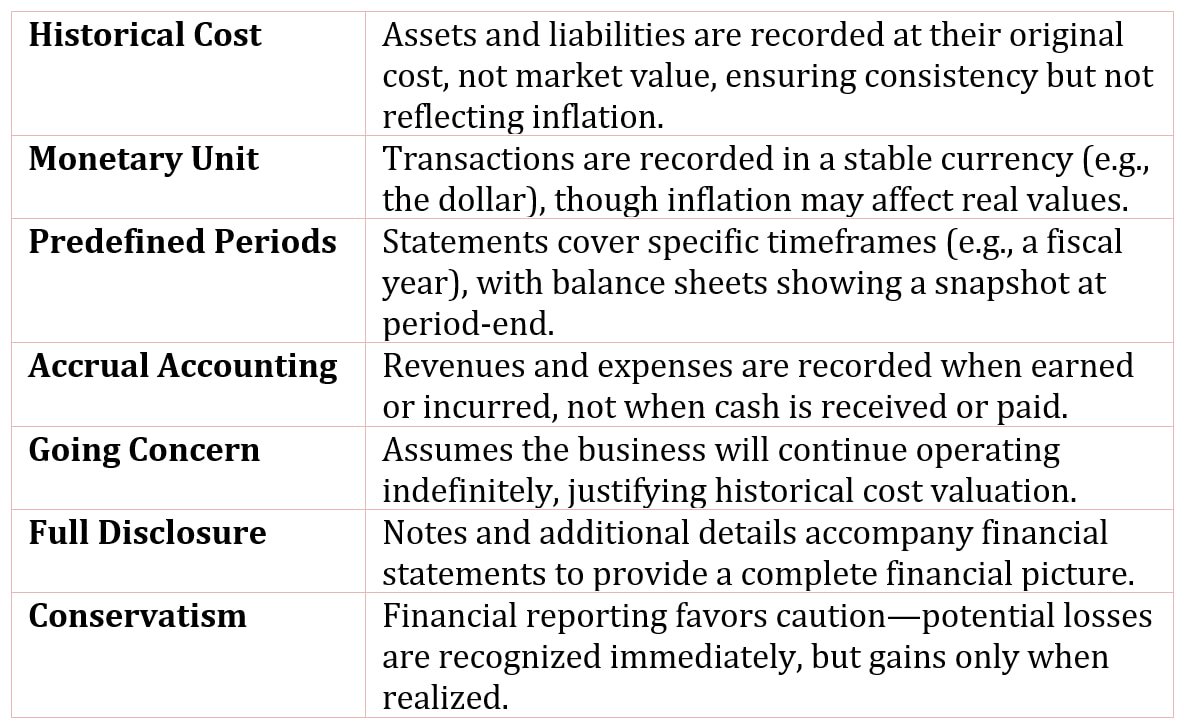
Table of Contents
The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial report that provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time, typically at the end of a fiscal quarter or year.
It outlines the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity, showing how resources are financed.
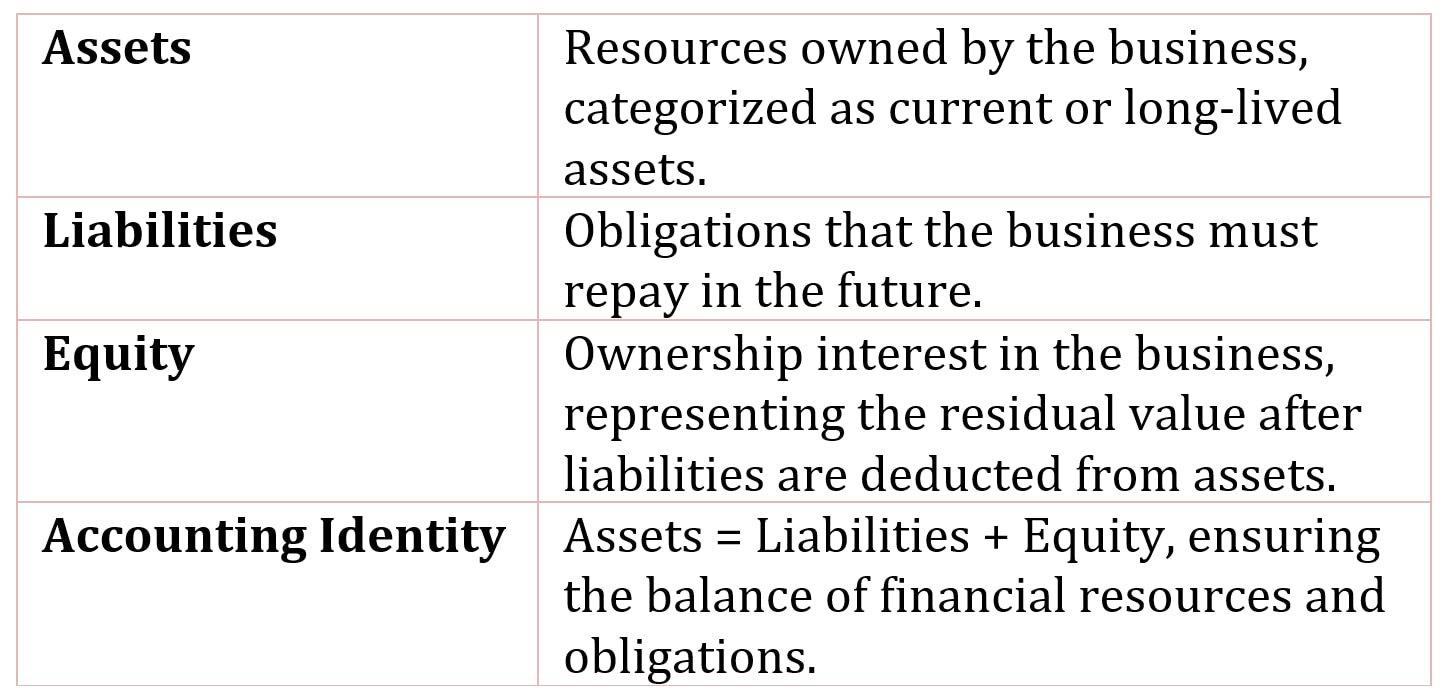
The components of the balance sheet are:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Equity
Assets
Assets are resources of the business enterprise, which are comprised of current or long-lived assets.
These resources are financed through liabilities and equity, where liabilities represent obligations to be repaid in the future, and equity reflects the ownership interest in the business.
Liabilities
Liabilities are obligations of the business enterprise that must be repaid at a future point in time.
Liabilities may be interest-bearing, such as a bond issue, or noninterest bearing, such as amounts due to suppliers.
Equity
Equity is the ownership interest of the business enterprise.
For a corporation, equity is the amount that investors paid the corporation for the stock when it was initially sold, plus or minus any earnings or losses, less any dividends paid.
The relation between assets, liabilities and equity is simple, as reflected in the balance of what is owned and how it is financed, referred to as the accounting identity:
Assets = Liabilities + Equity