Table of Contents
Depository Institutions
Depository institutions include commercial banks and thrifts. Thrifts include savings and loan associations, savings banks, and credit unions. As the name indicates, these entities accept deposits that represent the liabilities (i.e., debt) of the deposit-accepting institution.
With the funds raised through deposits and non-deposit sources obtained by issuing debt obligations in the financial market, depository institutions make loans to various entities (businesses, consumers, and state and local governments).
Commercial banks are the largest type of depository institution and will be the focus here. A commercial bank is a financial institution that is owned by shareholders and engages in accepting deposits and lending for a profit.
A bank may be owned by a bank holding company (BHC), which is a company that owns one or more banks.
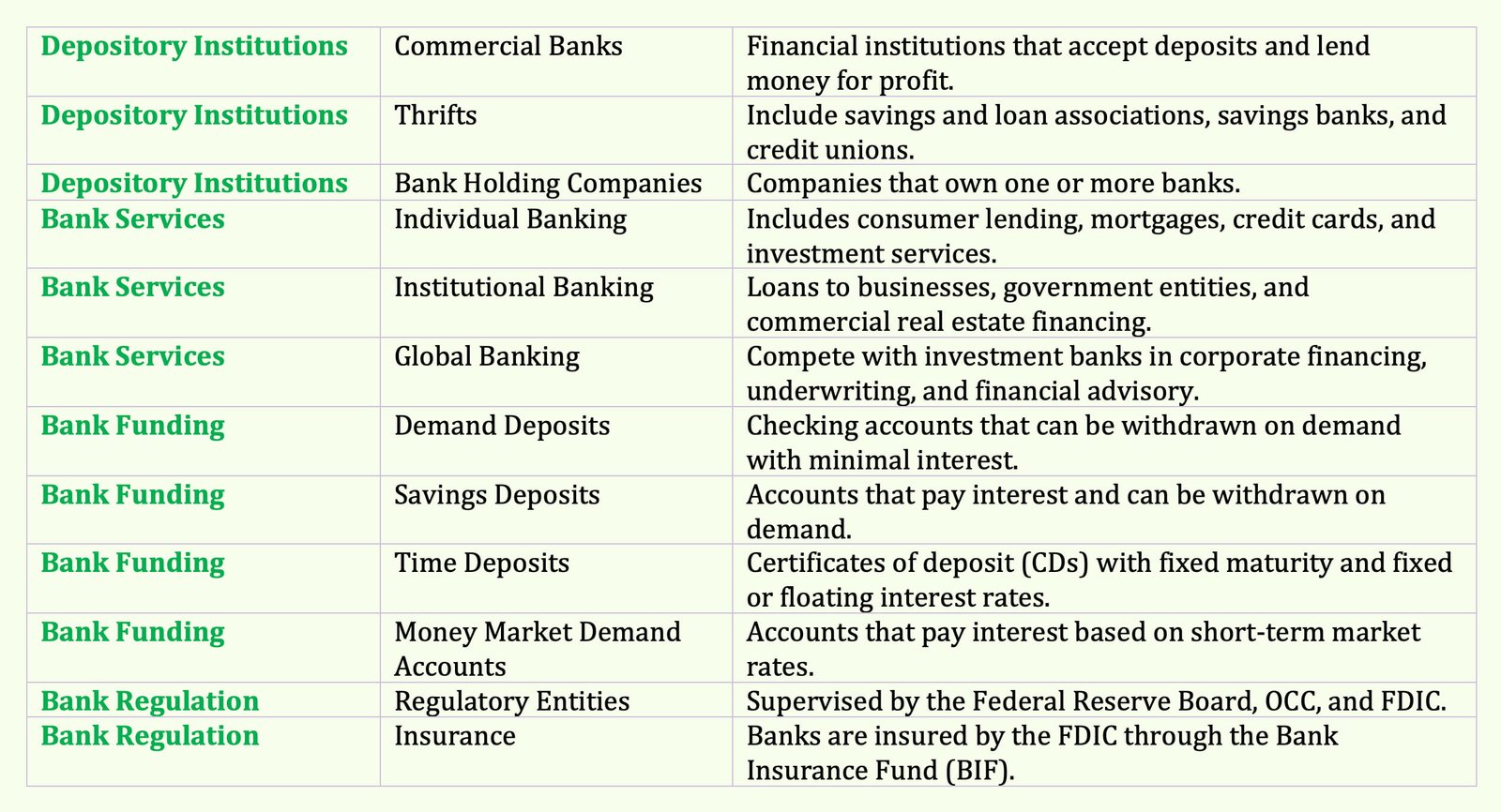
Bank Services
The principal services provided by commercial banks are:
- Individual banking
- Institutional banking
- Global banking
1. Individual Banking
Individual banking includes consumer lending, residential mortgage lending, consumer installment loans, credit card financing, automobile and boat financing, brokerage services, student loans, and individual-oriented financial investment services such as personal trust and investment services.
2. Institutional Banking
Institutional banking includes loans to both non-financial and financial business, government entities (state and local governments in the United States and foreign governments), commercial real estate financing, and leasing activities.
3. Global Banking
In global banking, commercial banks compete head-to-head with an other type of financial institution—investment banking companies.
In the global arena, banks engage in corporate financing that involves:
- Procuring of funds for a bank’s customers, which can go beyond traditional bank loans to involve the underwriting of securities and providing letters of credit and other types of guarantees;
- Financial advice on such matters as strategies for obtaining funds, corporate restructuring, divestitures, and acquisitions. Capital market and foreign exchange products and services involve transactions where the bank may act as a dealer or broker in a service.
Bank Funding
Banks are highly leveraged financial institutions, meaning that most of their funds come from borrowing. One form of borrowing includes deposits.
There are four types of deposit accounts issued by banks:
- Demand deposits
- Savings deposits
- Time deposits
- Money market demand accounts
1. Demand Deposits
Demand deposits, more popularly known as checking accounts, can be withdrawn upon demand and offer minimal interest.
2. Savings Deposits
Savings deposits pay interest (typically below market interest rates), do not have a specific maturity, and usually can be withdrawn upon demand.
3. Time Deposits
Time deposits, more popularly referred to as certificates of deposit or CDs, have a fixed maturity date and pay either a fixed or floating interest rate.
4. Money Market Demand Accounts
A money market demand account pays interest based on short-term interest rates.
Deposit sources other than borrowing that are available to banks are (1) borrowing by the issuance of instruments in the money and bond markets; (2) borrowing reserves in the federal funds market; and (3) borrowing from the Federal Reserve (Fed) through the discount window facility.
Bank Regulation
Because of their important role in financial markets, depository institutions are highly regulated and supervised by several federal and state government entities.
At the federal level, supervision is undertaken by the Federal Reserve Board, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC).
Banks are insured by the Bank Insurance Fund (BIF), which is administered by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. Federal depository insurance began in the 1930s, and the insurance program is administered by the FDIC.