Table of Contents
The Derivative Market
The derivative market is a financial marketplace where derivative instruments such as futures, options, forwards, and swaps are traded.
These financial contracts derive their value from an underlying asset, which can include stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, or market indices.
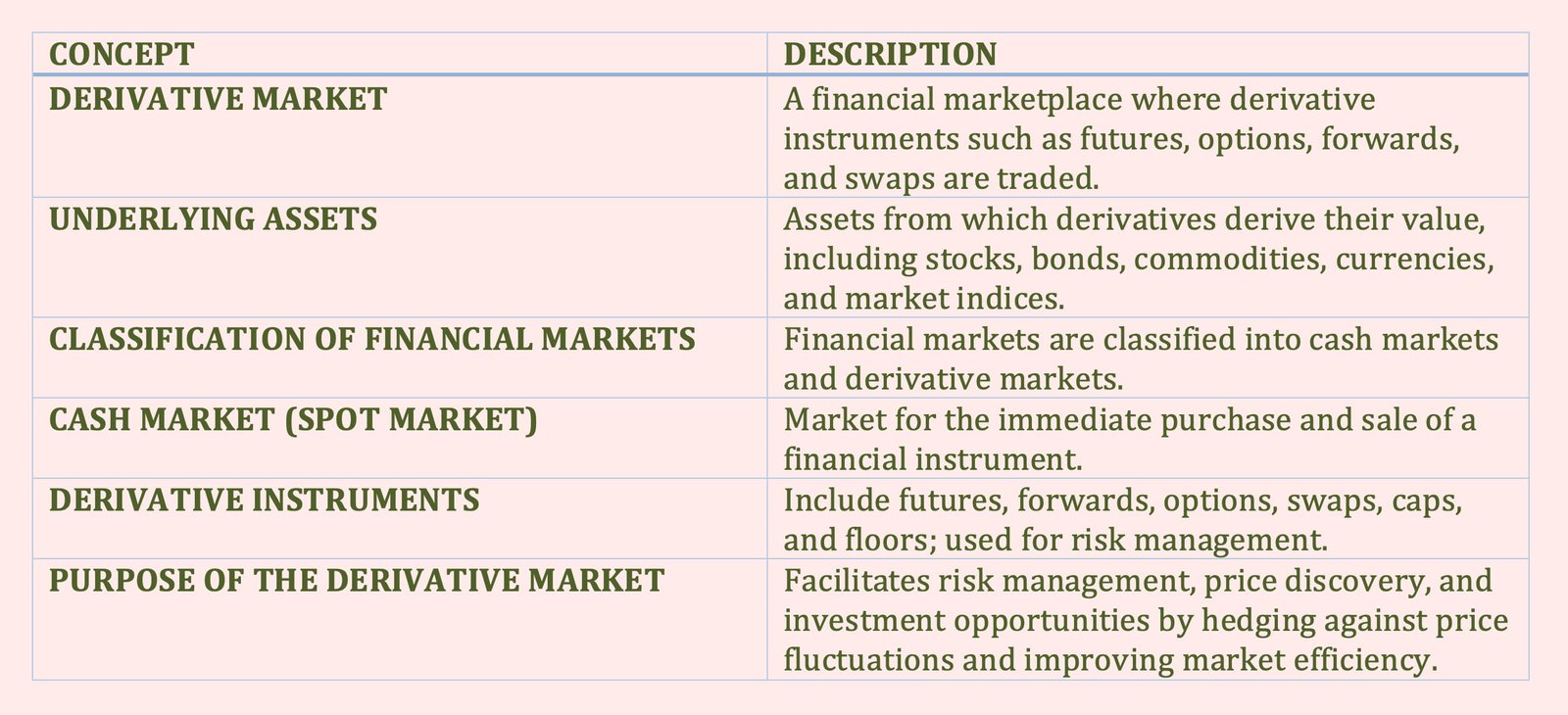
We classify financial markets in terms of cash markets and derivative markets.
The cash market, also referred to as the spot market, is the market for the immediate purchase and sale of a financial instrument.
In contrast, some financial instruments are contracts that specify that the contract holder has either the obligation or the choice to buy or sell something at or by some future date. The “something” that is the subject of the contract is the underlying asset or simply the underlying. The underlying can be a stock, a bond, a financial index, an interest rate, a currency, or a commodity.
Such contracts derive their value from the value of the underlying; hence, we refer to these contracts as derivative instruments, or simply derivatives, and the market in which they trade is the derivatives market.
Derivative Instruments
Derivative instruments, or simply derivatives, include futures, forwards, options, swaps, caps, and floors.
The primary role of derivative instruments is to provide a transactionally efficient vehicle for protecting against various types of risk encountered by investors and issuers.
Admittedly, it is difficult to see at this early stage how derivatives are useful for controlling risk in an efficient way since too often the popular press focuses on how derivatives have been misused by corporate treasurers and portfolio managers.
Purpose of the Derivative Market
The primary purpose of the derivative market is to facilitate risk management, price discovery, and investment opportunities.
The derivative market allows businesses, investors, and financial institutions to hedge against price fluctuations in underlying assets such as stocks, commodities, currencies, and interest rates.
By using derivatives like futures, options, swaps, and forwards, market participants can protect themselves from unfavorable price movements, thereby reducing uncertainty and financial risk.
The derivative market enhances market efficiency by improving liquidity and enabling accurate pricing of assets based on future expectations. It also provides opportunities for speculation, allowing traders to profit from market movements without directly holding the underlying asset.

